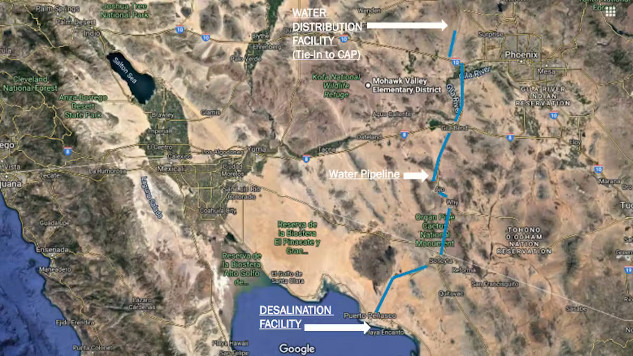
The proposed desalination plant in Mexico would pipe fresh water 200 miles to Arizona. Water Infrastructure Finance Authority of Arizona/ENR Southwest, CC BY-ND
Arizona is one of the fastest-growing states in the U.S., with an economy that offers many opportunities for workers and businesses. But it faces a daunting challenge: a water crisis that could seriously constrain its economic growth and vitality.
A recent report that projected a roughly 4% shortfall in groundwater supplies in the Phoenix area over the next 100 years prompted the state to curtail new approval of groundwater-dependent residential development in some of the region’s fast-growing suburbs. Moreover, negotiations continue over dwindling supplies from the Colorado River, which historically supplied more than a third of the state’s water.
As a partial solution, the Arizona Water Infrastructure Finance Authority is exploring a proposal to import desalinated water from Mexico. Conceptualized by IDE, an Israeli company with extensive experience in the desalination sector, this mega-engineering project calls for building a plant in Mexico and piping the water about 200 miles and uphill more than 2,000 feet to Arizona.
Ultimately, the project is slated to cost more than US$5 billion and provide fresh water at nearly 10 times the cost of water Arizona currently draws from the Colorado River, not including long-term energy and maintenance costs.
Is this a wise investment? It is hard to say, since details are still forthcoming. It is also unclear how the proposal fits with Arizona’s plans for investing in its water supplies – because, unlike some states, Arizona has no state water plan.
As researchers who focus on water law, policy and management, we recommend engineered projects like this one be considered as part of a broader water management portfolio that responds holistically to imbalances in supply and demand. And such decisions should address known and potential consequences and costs down the road. Israel’s approach to desalination offers insights that Arizona would do well to consider. A 20-year drought in the Colorado River basin poses critical questions for Arizona’s water future.
Lands and waters at risk
Around the world, water engineering projects have caused large-scale ecological damage that governments now are spending heavily to repair. Draining and straightening the Florida Everglades in the 1950s and ?60s, which seriously harmed water quality and wildlife, is one well-known example.
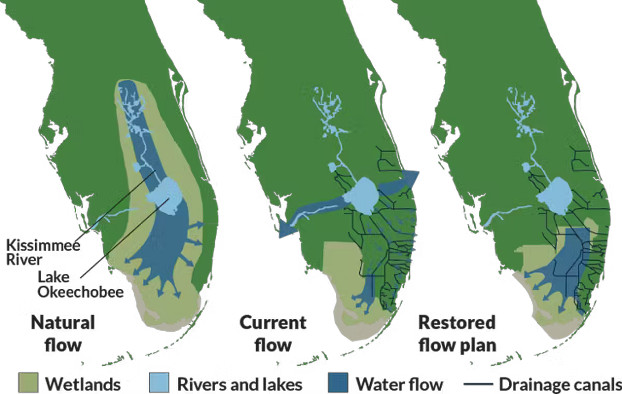
State and federal agencies are spending billions of dollars to restore the Everglades, reversing water control projects from 1948-1963 that channelized and drained these enormous wetlands. US Army Corps of Engineers/Florida Museum
Israel’s Hula wetlands is another. In the 1950s, Israeli water managers viewed the wetlands north of the Sea of Galilee as a malaria-infested swamp that, if drained, would eradicate mosquitoes and open up the area for farming. The project was an unmitigated failure that led to dust storms, land degradation and the loss of many unique animals and plants.
Arizona is in crisis now due to a combination of water management gaps and climatic changes. Groundwater withdrawals, which in much of rural Arizona remain unregulated, include unchecked pumping by foreign agricultural interests that ship their crops overseas. Moreover, with the Colorado River now in its 23rd year of drought, Arizona is being forced to reduce its dependence on the river and seek new water sources.
The desalination plant that Arizona is considering would be built in Puerto Peñasco, a Mexican resort town on the northern edge of the Gulf of California, also known as the Sea of Cortez. Highly saline brine left over from the desalination process would be released into the gulf.
Because this inlet has an elongated, baylike geography, salt could concentrate in its upper region, harming endangered aquatic species such as the totoaba fish and the vaquita porpoise, the world’s most endangered marine mammal.
The pipeline that would carry desalinated water to Arizona would cross through Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument, a fragile desert ecosystem and UNESCO biosphere reserve that has already been damaged by construction of the U.S.-Mexico border wall. To run the facility, IDE proposes to build a power plant in Arizona and lay transmission lines across the same fragile desert.
No single solution
Israel has adapted to water scarcity and has learned from its disastrous venture in the Hula wetlands. Today the country has a water sector master plan that is regularly updated and draws on water recycling and reuse, as well as a significant desalination program.
Israel also has implemented extensive water conservation, efficiency and recycling programs, as well as a broad economic review of desalination. Together, these sources now meet most of the nation’s water needs, and Israel has become a leader in both water technology and policy innovation.
Water rights and laws in Arizona differ from those of Israel, and Arizona isn’t as close to seawater. Nonetheless, in our view Israel’s approach is relevant as Arizona works to close its water demand-supply gap.
Steps Arizona can take now
In our view, Arizona would do well to follow Israel’s lead. A logical first step would be making conservation programs, which are required in some parts of Arizona, mandatory statewide.
Irrigated agriculture uses more than 70% of Arizona’s water supply, and most of the state’s irrigated lands use flood irrigation – pumping or bringing water into fields and letting it flow over the ground. Greater use of drip irrigation, which delivers water to plant roots through plastic pipes, and other water-saving techniques and technologies would reduce agricultural water use.
Arizona households, which sometimes use as much as 70% of residential water for lawns and landscaping, also have a conservation role to play. And the mining sector’s groundwater use presently is largely exempt from state regulations and withdrawal restrictions.
A proactive and holistic water management approach should apply to all sectors of the economy, including industry. Arizona also should continue to expand programs for agricultural, municipal and industrial wastewater reuse.
Desalination need not be off the table. But, as in Israel, we see it as part of a multifaceted and integrated series of solutions. By exploring the economic, technical and environmental feasibility of alternative solutions, Arizona could develop a water portfolio that would be far more likely than massive investments in seawater desalination to achieve the sustainable and secure water future that the state seeks.![]()
About The Author
Gabriel Eckstein, Professor of Law, Texas A&M University; Clive Lipchin, Adjunct Professor of Environmental Studies, Tel Aviv University, and Sharon B. Megdal, Professor of Environmental Science and Director, Water Resources Research Center, University of Arizona
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Books on The Environment from Amazon's Best Sellers list
"Silent Spring"
by Rachel Carson
This classic book is a landmark in the history of environmentalism, drawing attention to the harmful effects of pesticides and their impact on the natural world. Carson's work helped to inspire the modern environmental movement and remains relevant today, as we continue to grapple with the challenges of environmental health.
Click for more info or to order
"The Uninhabitable Earth: Life After Warming"
by David Wallace-Wells
In this book, David Wallace-Wells offers a stark warning about the devastating effects of climate change and the urgent need to address this global crisis. The book draws on scientific research and real-world examples to provide a sobering look at the future we face if we fail to take action.
Click for more info or to order
"The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They Communicate?Discoveries from A Secret World"
by Peter Wohlleben
In this book, Peter Wohlleben explores the fascinating world of trees and their role in the ecosystem. The book draws on scientific research and Wohlleben's own experiences as a forester to offer insights into the complex ways that trees interact with one another and the natural world.
Click for more info or to order
"Our House Is on Fire: Scenes of a Family and a Planet in Crisis"
by Greta Thunberg, Svante Thunberg, and Malena Ernman
In this book, climate activist Greta Thunberg and her family offer a personal account of their journey to raise awareness about the urgent need to address climate change. The book provides a powerful and moving account of the challenges we face and the need for action.
Click for more info or to order
"The Sixth Extinction: An Unnatural History"
by Elizabeth Kolbert
In this book, Elizabeth Kolbert explores the ongoing mass extinction of species caused by human activity, drawing on scientific research and real-world examples to provide a sobering look at the impact of human activity on the natural world. The book offers a compelling call to action to protect the diversity of life on Earth.